Computer Hardware
What is Hardware?
The physical portion of the computer
Examples of Computer Hardware
- Motherboard – The “baseplate”
- Processor – The "brain"”
- RAM – The quick read/write memory of a computer
- HDD/SSD – The storage of data
- PSU – The power
- Case – The house
- GFX – The “painter”
The Motherboard
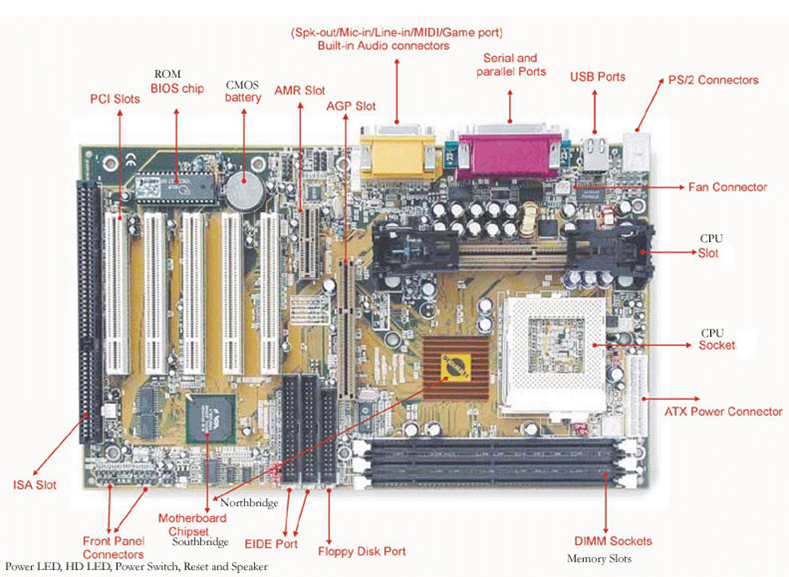
The motherboard (mobo) is filled with ports that all of the other parts connect to. The motherboard has a chipset which regulates the information between parts. The motherboard contains:
- DIMM Slots for RAM - Has either 2 or 4 for dual channel support
- CPU Socket - Drop the CPU in and secure it with a little lever
- PCI Slots - Slots that are widely used for extra addons such as graphics cards or extra USB 3.0 slots or WiFI adapters
- ATX Power Connector - A socket for power from the PSU to power the motherboard
- "Output Row" - Slew of female adapters that range from DVI, VGA, HDMI, USB, Ethernet, Audio Out/In, or PS/2 connectors
- SATA Slots - Used to connect HDDs and SSDs
The Processor

The central processing unit (CPU) is what computes the 0s and 1s. The clock is the speed in usually GHz or MHz. Most processors are quad-core.
RAM
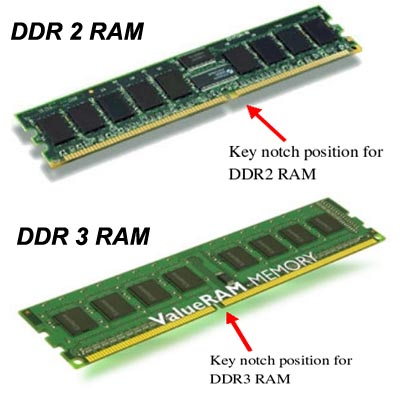
RAM is used to quickly store data that is used by a running program. RAM comes in 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, 8GB, 16GB and is clocked from 776 MHz to 2400 MHz.
Hard disc drive / Solid state drive
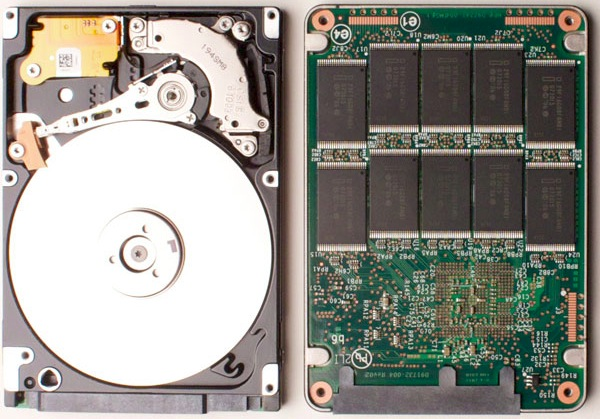
HDD/SSD is used to store data on the long term. HDDs use discs to read and write data while SSDs used NAND chips. SSDs have very fast read/write times, but they are more expensive.
Power Supply Unit

The PSU simply gives power to the computer.
Case

The Case simply gives a home to the computer parts.
Graphics Card

The graphics card is used to render the screen. It is also used to play jaw dropping games.